PPAR delta is important for heart function, energy production, endurance capacity, reducing inflammation and reducing obesity.
PPAR Delta Simple
PPARδ is a nuclear hormone receptor that governs a variety of biological processes and may be involved in the development of several chronic diseases, including diabetes, obesity, atherosclerosis, and cancer.
PPARδ may function as an integrator of sorts.
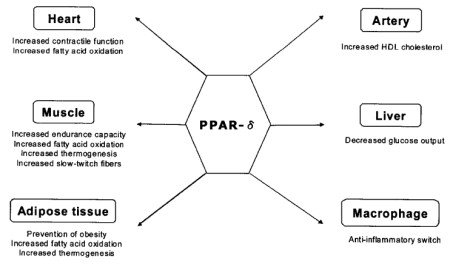
PPARδ helps prevent heart disease [1].
PPARδ is important for hair growth [2].
At higher levels, PPAR-δ increases fat burning in muscle and fat cells and increases energy expenditure. At lower levels, it helps create fat cells [3, 4].
PPARδ is found to be elevated in colorectal cancer cells.
Studies into the role of PPAR-δ in cancer have produced contradictory results and there is no scientific consensus on whether it promotes or prevents cancer formation [5].
PPARδ is involved with the absorption of fat and cholesterol (lipid uptake, such as fatty acid binding protein and fatty acid translocase). Also, it helps the growth of intestinal mucosa in response to fat [3].
PPARδ decreases inflammatory responses of macrophages and is linked to a significant rise in HDL cholesterol. PPAR activation in the liver decreases liver glucose output, thereby contributing to improved glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity [6].
In a meta-analysis, PPAR delta was associated with height [7].
PPAR Delta Advanced
PPAR delta decreases Cannabinoid receptor expression [8].
PPAR delta decreases inflammatory cytokines such as TNF and macrophage-related inflammation (R). PPARδ helps prevent TNFα-induced apoptosis in skin cells [3].
PPAR delta is a potent inhibitor of activation of PPAR alpha and PPAR gamma [9].
PPAR delta inhibits the Th1 and Th17 immune systems [10] and combats autoimmunity [11], and causes weight loss.
Treatment of obese animals by PPARδ activators results in normalization of metabolism and a reduction of body bat. PPARδ also can increase fat cells when on a high-fat diet by stimulating preadipocyte proliferation and by controlling the induction of PPAR gamma [3].
The nuclear receptor increases the fatty acid burning capacities of muscle and fat tissue by controlling the expression of genes involved in fatty acid uptake, β-oxidation, and energy uncoupling [3].
PPAR delta increases the production of PGC-1a and TGF-beta [12].
PPAR delta potentiates PPAR gamma fat cell production [13].
Well described target genes of PPARδ include PDK4, ANGPTL4, PLIN2, and CD36.
PPAR Delta SNPs: rs2016520 T294C
Check out Selfdecode to see if you have these genes.
- RS1053049 (PPARD) CC
- RS1883322 (PPARD) CC
- RS2016520 (PPARD) CT
- RS2076167 (PPARD) CC
- RS2076169 (PPARD) AA
- RS2267668 (PPARD) AG
- RS6922548 (PPARD) AG
How to Increase PPAR delta
- Endurance exercise… PPARD increases by more than twofold 3 hours following an acute bout of endurance exercise [15]
- Palmitoylethanolamide [16]
- Lion’s Mane [17]
- Arachidonic acid (omega-6’s convert to it) [5] – Hydroxyicosatetraenoic acid (metabolites of arachidonic acid)
- Cardarine (Research chemical: GW501516) [18]
- Berberine increases PPAR delta [19, 20]
- Growth hormone increases PPAR delta in animal models [21]
- Naringenin increases PPAR delta [22]
- Genistein and Daidzein
- Sun/UVB (skin) [23]
If you want to interpret your genes and see how they affect your PPAR Delta, you can upload them into SelfDecode.
SelfDecode is a sister company of SelfHacked. The proceeds from your purchase of this product are reinvested into our research and development, in order to serve you better. Thank you for your support.
